Pine Grosbeak
Pine grosbeaks are the larger members of the finch family found in the boreal forests. Sexual dimorphism is present among males and females. They are stocky, plump and heavy-chested with strong, short, and cone-shaped bills. The nine recognized subspecies of pine grosbeak vary in body size, bill shape and size, as well as in leg, tail and wing lengths.
Scientific Classification
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Aves |
| Order | Passeriformes |
| Family | Fringillidae |
| Genus | Pinicola |
| Species | Pinicola enucleator |
Quick Information
| Similar Species | House Finch, Purple Finch, White-winged Crossbill, Evening Grosbeak |
| Other Names | Pine Rosefinch |
| Size | 20-25.5 cm (7-10 in) long |
| Wingspan | 12-13 in |
| Weight | 52-78 g (1.8-2.8 oz) |
| Color | Adults possess a long black tail and wings and white wing bars; red back and head in males; olive-yellow head with gray back and under parts in females; juveniles have dull colors |
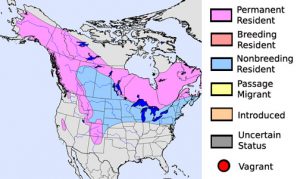
| Distribution | Alaska, Canada, mountains of the Western United States, Siberia, Subarctic Fennoscandia |
| Habitat | Coniferous, Deciduous, and mixed forests as well as cities and suburban areas |
| Nesting | May – July |
| Sounds | Their call includes a whistled pui pui pui or chii-vii; songs consist of clear, warbling, flute-like notes; flight calls are like tee-tee-tew |
| Lifespan | Up to 9.8 years in the wild |
| Diet | They feed on seeds, fruits, and buds; occasionally eat insects |
| Clutch Size | 2-4 eggs |
| Number of Broods | 1 per year |
| Incubation Period | 13-14 days |
| Predators and Competition | Wolves, lynxes and hawks |
| IUCN Conservation Status | Least Concern |

Pine Grosbeak Images
Behavior
They travel from one place to another in search of food, foraging in shrubs and trees. During the breeding season, they usually remain in pairs; however, they remain in larger flocks the rest of the year.
Breeding and nesting
Pine grosbeaks are monogamous. They typically build their nest in dense foliage on horizontal branches close to the trunk of the tree. Females usually build the nest, which is made up of twig lined with grass, moss, and lichen.
Lifecycle
During incubation, the male brings food for the female. After hatching, both male and female feed the young. Fledging takes place after about 2 weeks from hatching. Sometimes the young ones depend on their parents for food even after fledging.
Interesting Facts
- They are quite vocal and are known to mimic the songs and calls of other species.
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pine_grosbeak
- https://www.allaboutbirds.org/guide/Pine_Grosbeak/id
- http://www.audubon.org/field-guide/bird/pine-grosbeak
- https://abcbirds.org/pine-grosbeak
- https://nhpbs.org/wild/pinegrosbeak.asp
Published on July 23rd 2016 by Sajal Datta under Coniferous Forest Animals.
Article was last reviewed on 17th July 2023.