Yellow-bellied Flycatcher
The Yellow-bellied Flycatcher is a species of small passerines of the tyrant flycatcher family. Its broad range of distribution makes its population relatively invulnerable for some time to come.
Scientific Classification
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Aves |
| Order | Passeriformes |
| Family | Tyrannidae |
| Genus | Empidonax |
| Scientific Name | Empidonax flaviventris |
Quick Information
| Also Known As | Moucherolle à ventre jaune (French), Mosquareta barriga-amarilla, Mosquerito de vientre amarillo (Spanish) |
| Similar Species | Pacific-slope Flycatcher, Cordilleran Flycatcher |
| Size | 5.1-5.9 in (12.9-14.9 cm) |
| Wingspan | 7.1-7.9 in (18-20 cm) |
| Weight | 0.3-0.6 oz (8.5-17 g) |
| Color | Adults: Greenish above and yellowish below, with a dark-colored breast; white or yellow eye-ring and wing-bars, upper mandible is dark while the lower one is pinkish-orange Juveniles: Similar to adults |
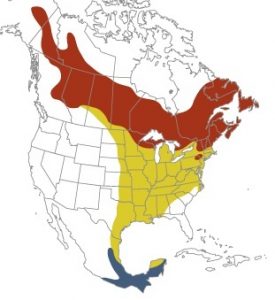
| Range of Distribution | Northeastern United States and Throughout Canada, migrates to Central America |
| Habitat | Breeding: Peatlands and coniferous forests Nesting: Swamps, bogs, and moist forests Winter: Dense rainforests, pine-oak forests, montane evergreen forests and shaded coffee plantations |
| Sounds | Songs heard mostly during flight at dawn and dusk; described as ‘chiu chiu’, ‘pse-k’, ‘chebek’; distinctive calls include a ‘chu-wee’, with the pitch slowly ascending, a rough, sharp ‘peeek’ and a softer ‘pyuuu’, with a descending pitch |
| Lifespan | Around 5 years 2 months |
| Diet | Insects and arthropods, sometimes eats fruits |
| Adaptations | They can hover in flight; this aids them in picking insects from leaves without having to land |
| Clutch Size | 2-5 |
| Incubation Period | 12-14 days |
| Predators | Likely to be preyed on by snakes and birds of prey |
| IUCN Conservation Status | Least Concern |
Behavior
Yellow-bellied flycatchers are secretive birds, even during the breeding season they stay inconspicuous and as such are difficult to locate. They forage by perching at low to medium heights in the forest and flying out and catching insects in mid-air. They also pick insects from foliage and sometimes even from the perch itself. Males are territorial and actively chase away other intruding males.
Mating & Reproduction
These monogamous animals breed between May and August. Females build a cup-shaped nest on or near the ground and line it with moss and plant parts; nests are very well hidden. Incubation is done by the female.
Life-cycle
Baby yellow-bellied flycatchers are featherless and helpless when hatched from the brown-spotted white eggs; they are looked after by both parents before fledging at around 13 days old. Sexual maturity is reached at the age of 1 year.
Interesting Facts
- Some yellow-bellied flycatcher sightings have been reported from Greenland.
- The nests of yellow-bellied flycatchers are often used by brown-headed cowbirds for laying their eggs.
References:
- https://www.allaboutbirds.org/guide/Yellow-bellied_Flycatcher/lifehistory
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Yellow-bellied_flycatcher
- https://www.beautyofbirds.com/yellowbelliedflycatchers.html
- http://www.audubon.org/field-guide/bird/yellow-bellied-flycatcher
- http://www.uwgb.edu/birds/greatlakes/species/ybfl.htm
Published on September 19th 2016 by Sudipto Chakrabarti under Coniferous Forest Animals.
Article was last reviewed on 5th December 2024.